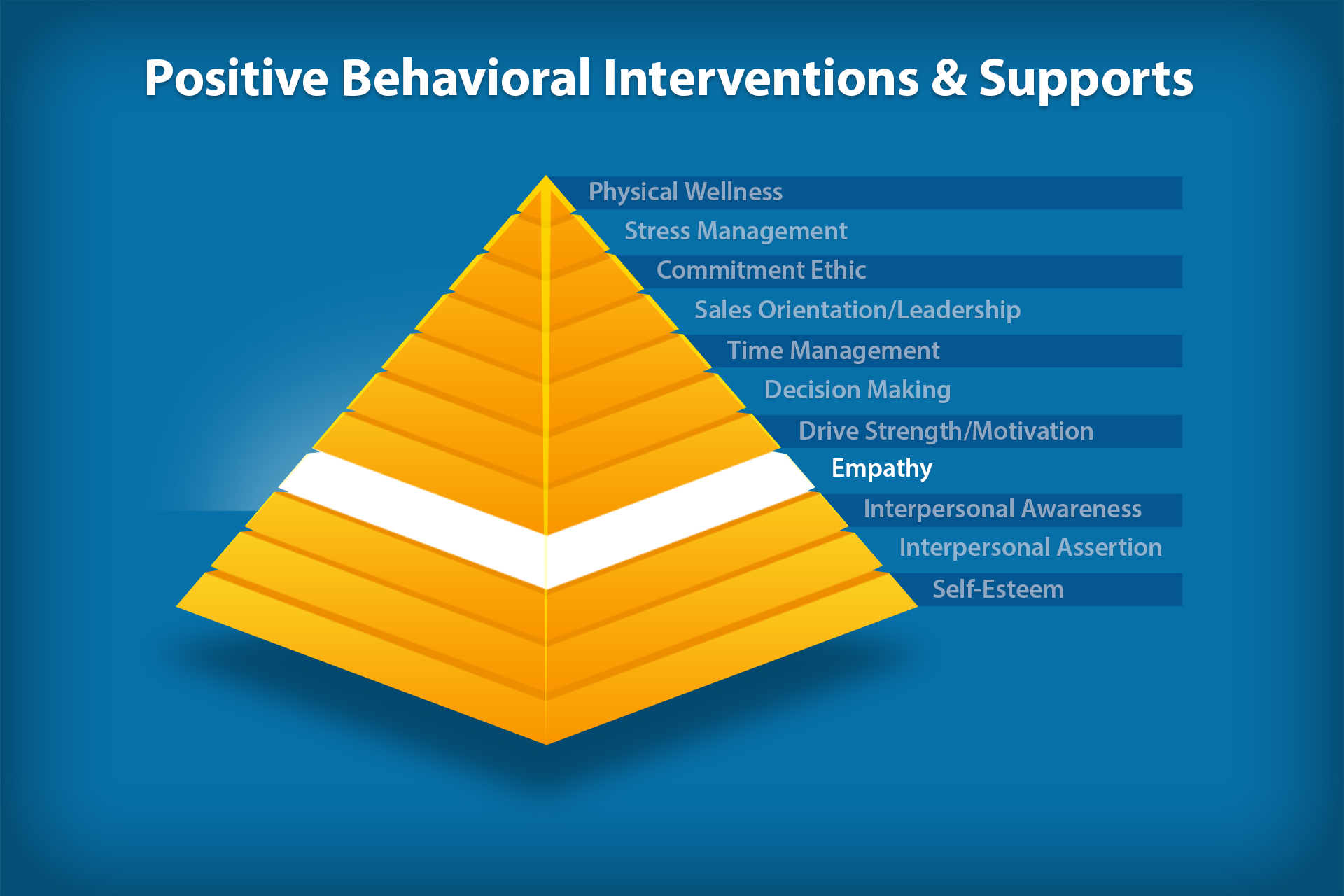
Empathy: The Cornerstone of Emotional Intelligence
Empathy is the fourth building block of our social/emotional pyramid that is measured by the Success Profiler’s Personal Skills Map. Empathy is one of the most critical characteristics of social and emotional learning (SEL). Without empathy, emotional intelligence is simply not possible.
Empathy is also a critical skill for making the PBIS framework successful in any school. PBIS (Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports) is a proactive approach to establishing the behavioral supports needed for students to achieve social, emotional and academic success. PBIS brings together the worlds of academic instruction and behavioral interventions.
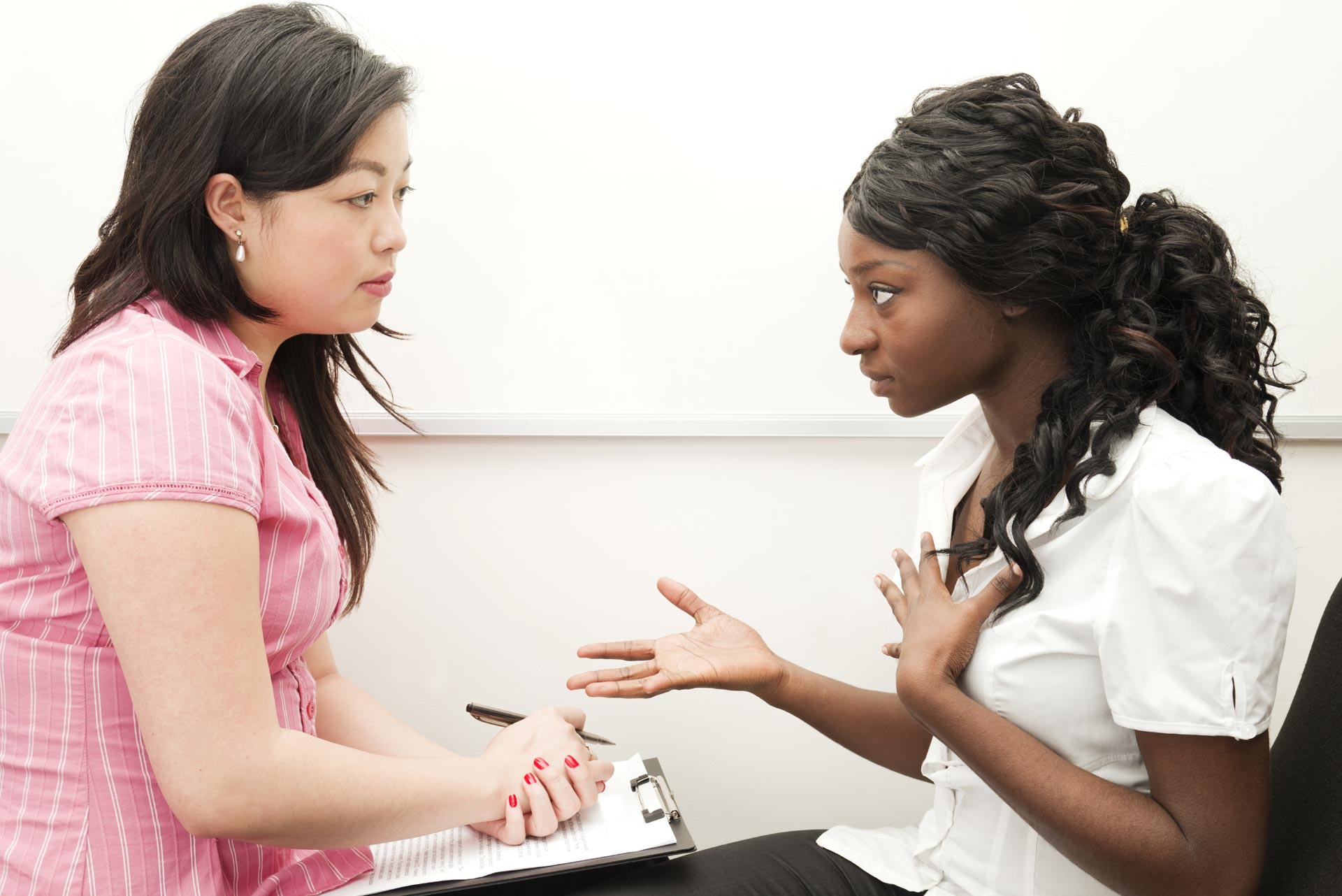

Broadly, empathy is the ability to communicate and lead by understanding the thoughts, views and feelings of others. As you know, no two people share the same thoughts. Our thoughts and experiences play a huge role in how we see the outside world. In order to truly understand another person, we need to understand his or her thoughts, feelings and experiences.
Everyone practices empathy in one way or another. If we are paying attention to what other people are saying, we are empathizing with them. We become involved in their feelings and thoughts in order to better understand who they are and what they want or need. We can respond to what they are saying.
Listening: The key for developing empathy
Better listening leads to:
- better understanding of people
- fewer mistakes and misunderstandings
- a chance to learn more
- better ability to work together
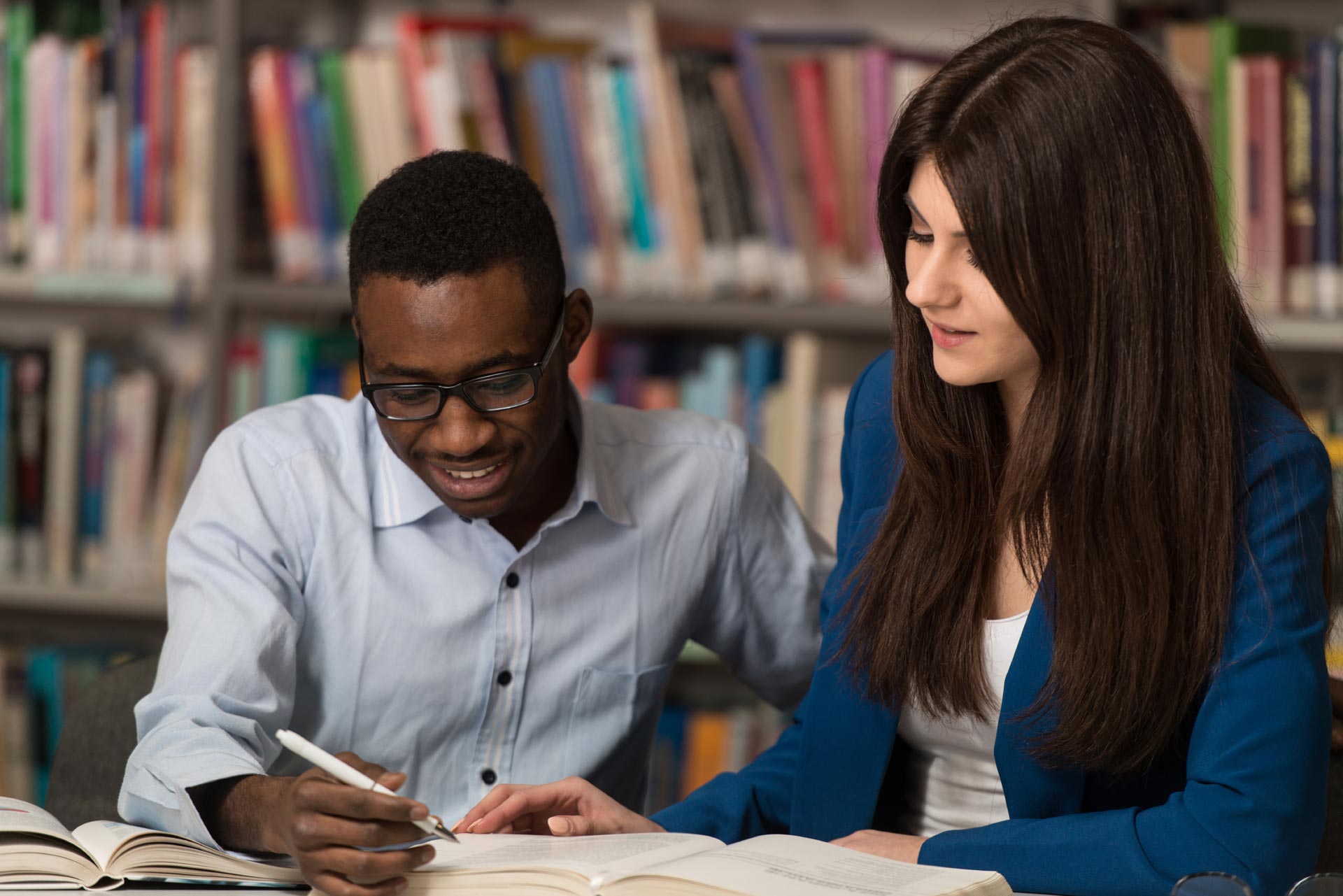

Empathetic Listening: A step beyond
Empathetic listening is a type of listening that goes further than ordinary listening. This type of listening uses another person’s point of view to see the world. It provides a higher level of understanding of how others feel.
There are four stages to empathetic listening:
Stage 1: Copy what is said. Repeat what you hear in order to gain further understanding. Repeat it exactly as you think you heard it.
Stage 2: Say what you hear. Repeat the words that were said without adding anything new.
Stage 3: Reflect on the feeling. Try to understand the feeling expressed in what was said, going beyond what you think you heard.
Stage 4: Restate what was said and think about the feeling. This combines stages 2 and 3 in order to understand the message.
But, just knowing about Empathy isn’t going to translate into positive outcomes for your program. If you really want to see results, you need to apply this information in a way that will help the individuals you work with set goals, manage their emotions, and develop the workplace readiness skills they need to be successful in today’s information economy.
If you need help connecting PBIS to meaningful outcomes, we’ve developed social/emotional learning standards that you can download for FREE. These standards are research-based and organized by stage of life, so you can easily identify which skills to work on with your users or students.
If you’d like to download our soft skills standards you can find them here:
